PySpark Install
PySpark
Install
Environement: WSL ubuntu 18
Conda
install anaconda and create a new environment with python=3.6
Environement: WSL ubuntu 18
install anaconda and create a new environment with python=3.6
The simplest way is
1 | pip install --pre -i https://pypi.anaconda.org/scipy-wheels-nightly/simple scipy |
However it is just a preview version of spicy, remember to updata it afterwrds.
本来想自己写的,但是这篇文章写得太好了,几乎没有死角,所以就在以下简单写写补充的内容好了。
VC dimension is a measurement of model complexity. VC dimension \(\alpha\) # of model parameters.
Depress overfitting => Limit model complexity => Limit VC dimension => Limit number of model parameters => Dropout/Regularization (Dropout can also been seen as a special regularization)
L0 norm = number of non-zero parameters.
It would be a good idea to add L0 norm to the Loss function.
方法1:opencv
opencv可以通过一些操作(主要通过canny和扩张腐蚀)得到特定的轮廓
但是实际操作下来感觉非常依赖参数的调整和图像预处理,很不稳定,并且道路本身的一些特征(如道路接缝)也会被检测
方法2:deeplearning
由于Road Damage Detection是一个在深度学习领域很成熟的话题。我直接搜索了相关的竞赛。
目前排名较高的均为使用YOLO实现,我自己也进行了尝试(YOLO v5)但是效果很不理想,几乎检测不到。
这个领域我还没有深入探索。但是如果我们没有对检测速度很高要求的话,使用maskRCNN或许是更加适合的方案。
This article in written in 2021.10.27, and current version is
0.1a3. In the future, Apple may provide a better machine
learning structure on TensorFlow, so please always remember to check here.
My feeling: 🐂🍺 but lots of bugs
Article reference.
xcode-select --installwhich xcrun, you should get the path to
xcrunMiniforge is just a substitude of Anaconda.
Follow the instruction here.
如何实现shuffle
1 | // pseudocode |
手写排序算法(quicksort为什么最快)
1 | void Quick_Sort(vector<int>& vec, int start_index, int end_index) |
QuickSort为什么最快?
QuickSort为什么不够快?
worst situation:quicksort对pivot选择要求很高,最坏情况会退化成bubble,所以对pivot选择要求很高,而STL中也对quicksort进行了优化--使用introspective sort
stable:quicksort总体上stable,但不能保证stable
在特殊情况下使用bucket sort还会更快
对于处理linked list,cache locality就不复存在,quicksort没有优势,常使用merge sort,此时也不需要额外空间。数据库中sort也常使用disk mergesort
Listen to a conversation between a student and a library employee. Excuse me, I received a letter that I am supposed to return the book that I checked out back in September. It is called Modern social problems. But I am writing my senior thesis. So I thought I was allowed to keep the book for the whole academic year. So you signed up for ‘extended borrowing privileges’. And we are still asking you to bring this book back? You can keep it all year as long as no one else request it. But some one else has, it looks like one of the professors in sociology department, so you have to bring it back. You can check it out again when it is returned in a couple of weeks. So what if the person renews it and I really need it right now. Is there a certain section or chapter you are working with? There is one chapter I am particular working with. Because of the circumstances, we can photocopy up to one chapter of the book for you. Why do not you do that for the one you are working with right now. By the time you need the rest of the book, maybe it will have been returned. Is it okay if I bring that by in a couple of days? Actually the due day is tomorrow. After that, there will be a two-dollar per day fine. But you need to return it today if you want to check out any books today. That’s out policy. No a lot of people realize that. In fact, every semester we get a few students who have had their borrowing privileges suspended completed because they haven’t return books. They are allowed to use books only in the library. They are not allowed to check anything out because of unreturned books. That is not good. I guess I should head back down to the dorm room right now. Before you go what you should do is fill out a form requesting the book back in two weeks. Then the person who requested it won’t be able to renew it, and you will get it back quickly.
针对一元函数 \(y=f(x)\),导数 \(f'(x_0)\) 表示了该函数在\(x_0\)处的函数斜率/增加速率。
针对多元函数(此处考虑二元函数\(z=f(x,y)\)),导数 \(f'(x_0, y_0)\) 就有些模糊不清了,为此我们先简化到一元的情况:固定 \(y=y_0\),\(z=f(x,y)\),二元函数便降纬为\(z=f(x, y_0)\) ,此时我们可以定义在 \(x\) 方向上的偏导数 \(f'_x(x_0, y_0)\),其表示该函数在\((x_0, y_0)\)点处沿 \(x\) 方向函数斜率/增加速率。类似的我们可以得到在 \(y\) 方向的偏导数。
由偏导数,我们已经可以得到 \(z\) 在 \(x=x_0\) 或 \(y=y_0\) 方向上的函数速率变化了。
现在基于这两个偏导数我们已经可以求出 \(x-y\) 平面任何方向的导数了:假设求 \(z\) 在 \(u=cos\theta \ \vec{i}+sin\theta \ \vec{j}\) 方向的导数(其中\(\theta\)表示该向量方向与\(x\)轴正方向的夹角,\(\vec{i}\)表示\(x\)轴正方向,\(\vec{j}\)表示\(y\)轴正方向) \[ D_uf(x,y)=\lim_{x \to \infty}\frac{f(x_0+tcos\theta,y_0+tsin\theta)}{t} \] 本质上方向导数是偏导数的一种推广,通过调整方向导数中 \(\theta\) 的值也能够简化为偏导数形式。
但是如果我们观察 \(u\) 本身,在 \(u\) 方向求导,其实相当于在 \(x\),\(y\) 方向分别求偏导之后的线性组合: \[ D_uf(x,y)=cos\theta f'_x(x,y)+sin\theta f'_y(x,y) \] ### Gradient
由偏导数,我们已经可以得到 \(z\) 在 \((x_0, y_0)\) 点上在方向 \(u=cos\theta \ \vec{i}+sin\theta \ \vec{j}\) 方向上的函数变化速率了。
那么梯度是什么呢?梯度就是 \(z\) 在 \((x_0, y_0)\) 点上函数变化速度最快的方向,也就是方向向量最大的方向。
什么时候方向向量能取到最大呢?
\(D_uf(x,y)=\begin{bmatrix}f'_x(x,y)&f'_y(x,y)\end{bmatrix}\begin{bmatrix}cos\theta \\ sin\theta\end{bmatrix}=\pmb A*\pmb I\),当 \((cos\theta, sin\theta) // (f'_x(x,y), f'_y(x,y))\) 时能够取到最大值,此时在 \((x_0,y_0)\) 的梯度 \(\pmb I=\begin{bmatrix}\frac{\partial f}{\partial x_0} \\ \frac{\partial f}{\partial y_0}\end{bmatrix}\)
梯度本质是矢量,在其方向上该点的方向向量最大。
IoU(Intersection over union): 两个bounding box( ground truth + proposed)之间重合部分的比例. \(IoU=\frac{A \cap B}{A \cup B}\)
TP(True positive): 对于所有ground truth检测IoU>=IoUthreshold(IoUthreshold一般取0.5)--有多少真实的bounding box被detect到(一个ground truth只考虑一次)
FP(False positive): 对于所有ground truth检测IoU<IoUthreshold(IoUthreshold一般取0.5)--每个ground truth有多少无效(IoU过低)/多余(多次检测同一个)的检测框
FN(False negative): 有多少真实的bounding box没有被detect到(一个ground truth只考虑一次)
Precision = \(\frac{TP}{TP+FP}\)--在检测为真的bounding box中有多少是有效的: \(Precision=\frac{TrueSamplesDetected}{AllDetecion}\)
Recall = \(\frac{TP}{TP+FN}\)--ground truth的bounding box有多少能被检测到: \(Recall=\frac{TrueSamplesDetected}{AllTrueSamples}\)
PR Curve: recall(x)-precision(y) curve
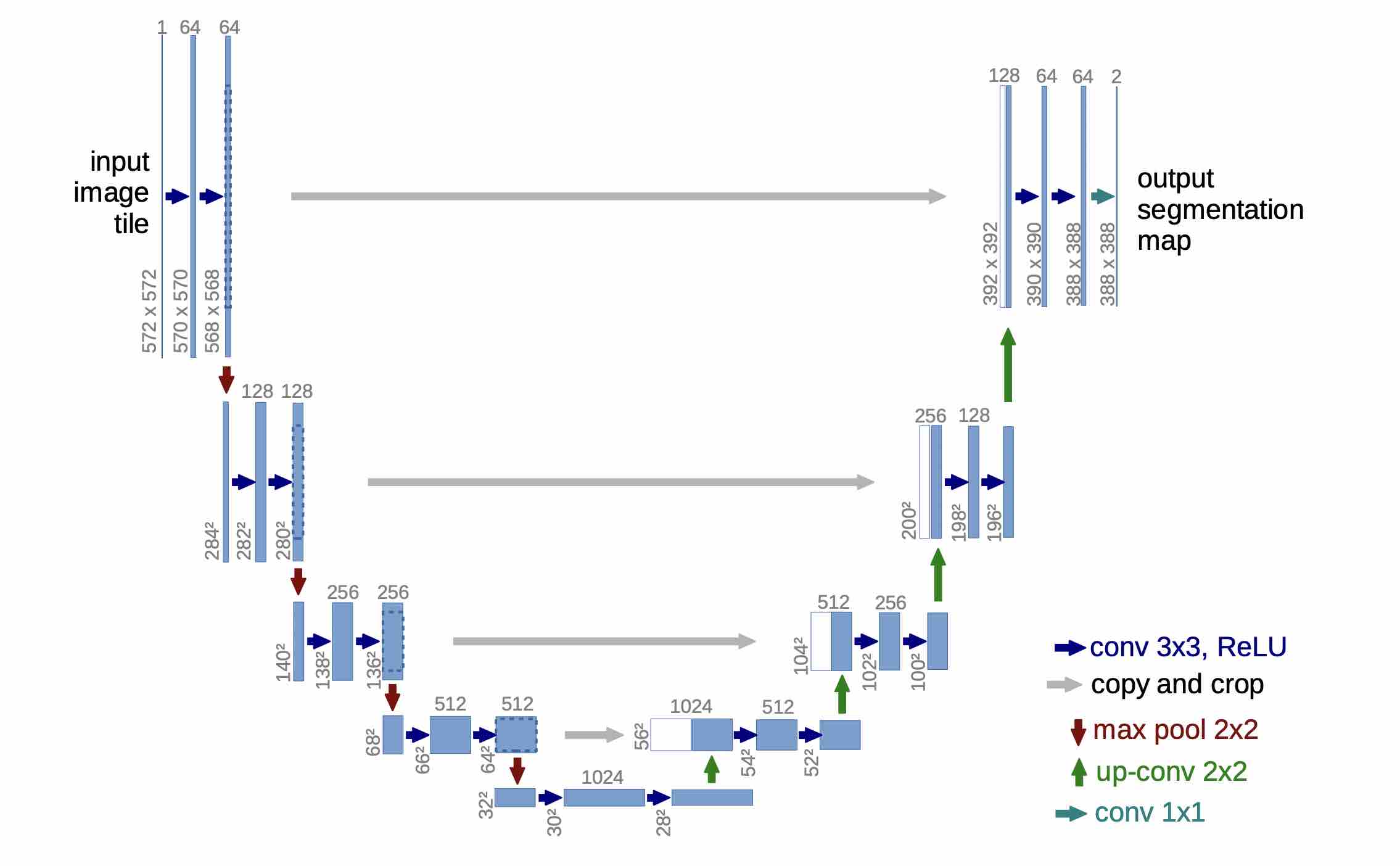
The structure of Unet is symmetric, like a shape of 'U'.
On the right side the blue box is feature map derived by convolution-deconvolution. And the white box is the just the same as the blue box on the left side. The grey arrow shows skip-connection-- putting the two parts together.
The encoder part is quite simple--3x3 convolutional kernel + maxpooling.
The decoder part is designed to restore the original shape of the image using upsampling.
In Unet, upsampling is implmented in bilinear interpolation.
torch.nn.Upsample(mode=bilinear)
Since upsampling will lose the detailed information of orginal image, Unet try to use skip-connection to fix this problem.
torch.cat([low_layer_features, deep_layer_features], dim=1)
(Note: In FCN, two parts are added in pixel level, however, in Unet, two part are concatenated together.--concatenating remains more details with more time consumed).